ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम (Operating System)
꧁ Digital Diary ༒Largest Writing Community༒꧂
एक Operating System (OS) एक system software है जो computer hardware और user के बीच एक interface का काम करता है। यह computer के resources को manage करता है और applications को run होने का environment provide करता है।
Imagine कीजिए:
Computer Hardware → एक office की building
Operating System → Office Manager
Application Software → Office के different employees
User → Office का owner
Operating System एक Office Manager की तरह work करता है:
Resources allocate करता है
Work coordinate करता है
Problems solve करता है
सब कुछ smoothly चलाता है
Process Management
Programs को run करना
CPU time allocate करना
Different processes के बीच switch करना
Memory Management
RAM का management करना
Programs को memory allocate करना
Virtual memory manage करना
File Management
Files create, delete और organize करना
Data store और retrieve करना
Folders और directories manage करना
Device Management
Keyboard, mouse, printer जैसे devices control करना
Device drivers manage करना
Input/output operations handle करना
Security Management
User authentication करना
Data protection provide करना
Access control manage करना
Windows OS - Microsoft company द्वारा बनाया गया
macOS - Apple company के computers के लिए
Linux - Open source operating system
Android - Mobile devices के लिए
iOS - Apple के mobile devices के लिए
Single-User OS - एक समय में एक user
Multi-User OS - एक समय में multiple users
Real-Time OS - Immediate response required
Network OS - Networks manage करने के लिए
Mobile OS - Smartphones और tablets के लिए
Kernel - OS का core part, सबसे important functions handle करता है
Shell - User और OS के बीच interface provide करता है
File System - Data store और organize करने का तरीका
Hardware Manage करता है - सभी devices को control करता है
User-Friendly Interface provide करता है
Resources Efficiently Use करता है
Security Provide करता है
Applications Run करने allow करता है
Example: जब आप:
Mouse click करते हैं → OS movement detect करता है
Keyboard type करते हैं → OS characters process करता है
Program open करते हैं → OS memory allocate करता है
File save करते हैं → OS storage manage करता है
Graphical User Interface (GUI) - Icons और windows through interact करना
Multitasking - एक साथ multiple programs run करना
Networking - Internet और networks connect करना
Plug and Play - Automatic device detection
Automatic Updates - Security और features improve करना

सिस्टम बूटिंग वह प्रक्रिया है जब कंप्यूटर को चालू (Power On) करने पर ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम मेमोरी में लोड होता है और कंप्यूटर उपयोग के लिए तैयार होता है। इसे कंप्यूटर का स्टार्टअप प्रोसेस भी कहते हैं।
कल्पना कीजिए:
कंप्यूटर बंद अवस्था → सोया हुआ इंसान
पावर बटन दबाना → इंसान को जगाना
बूटिंग प्रोसेस → उठना, तैयार होना, काम के लिए तैयार होना
ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम लोड होना → दिमाग का पूरी तरह काम करना
Power On Self Test (POST)
कंप्यूटर चालू होते ही Hardware की जांच होती है
RAM, Keyboard, Mouse, Disk Drives की testing होती है
अगर error होती है तो Beep Sound आती है
BIOS/UEFI Load होना
Basic Input Output System activate होता है
Hardware और Software के बीच connection establish होता है
Boot Device का order set होता है
Bootloader Load होना
Master Boot Record (MBR) read होता है
Bootloader program load होता है
Examples: GRUB (Linux), NTLDR (Windows)
Operating System Load होना
OS Kernel Memory में load होता है
Device Drivers Initialize होते हैं
System Services Start होती हैं
Login Screen आना
OS पूरी तरह Load हो जाता है
User Login के लिए तैयार होता है
Cold Booting
कंप्यूटर को Complete Shut Down के बाद Start करना
Full Startup Process होता है
Example: Power Button दबाना
Warm Booting
कंप्यूटर को Restart करना
POST Process skip हो सकता है
Example: Ctrl + Alt + Delete दबाना
BIOS (Basic Input Output System)
Motherboard पर stored firmware
Hardware Initialize करता है
MBR (Master Boot Record)
Hard Disk का first sector
Bootloader information store करता है
Bootloader
OS Kernel को Load करता है
Examples: GRUB, NTLDR, Bootmgr
Kernel
OS का Core Component
System Resources Manage करता है
Traditional BIOS की जगह UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) आया है
Faster Boot Time
Better Security Features
Large Hard Drives Support
Graphical Interface
Boot Device Not Found - Hard Disk Detect नहीं होना
Operating System Not Found - OS Corrupt होना
BOOTMGR is Missing - Windows Boot Manager Missing
Kernel Panic - Linux OS में Error
Infinite Boot Loop - Continuous Restarting
Windows Booting
BIOS/UEFI → Bootmgr → winload.exe → Kernel Load → Login Screen
Linux Booting
BIOS/UEFI → GRUB → Kernel Load → init Process → Login Screen
Mac Booting
EFI → boot.efi → Kernel Load → Launchd → Login Screen
Startup Programs कम करें
SSD Hard Disk Use करें
Regular Updates Install करें
Unnecessary Services Disable करें
Disk Cleanup Regularly करें
बूटिंग कंप्यूटर की वह शुरुआती प्रक्रिया है जब आप पावर बटन दबाते हैं और कंप्यूटर तैयार होकर लॉगिन स्क्रीन दिखाता है। इसे कंप्यूटर का स्टार्टअप भी कहते हैं।
कल्पना कीजिए:
कंप्यूटर बंद है → गाड़ी इंजन ऑफ है
पावर बटन दबाना → गाड़ी की चाबी घुमाना
बूटिंग प्रोसेस → इंजन स्टार्ट होना, सभी सिस्टम चेक होना, गाड़ी चलने के लिए तैयार होना
ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम लोड होना → ड्राइवर का बैठना और गाड़ी को हैंडल करना
पावर ऑन करना
जब आप कंप्यूटर का पावर बटन दबाते हैं
electricity supply शुरू होती है
BIOS/UEFI चलना
BIOS = Basic Input Output System
यह motherboard पर stored एक program है
सबसे पहले hardware की जांच करता है (RAM, keyboard, disk)
POST प्रक्रिया
POST = Power On Self Test
सभी hardware components check होते हैं
अगर error होती है तो beep sound आती है
Boot Device ढूंढना
BIOS boot order check करता है
पहले CD/DVD, फिर USB, फिर Hard Disk में OS ढूंढता है
Bootloader लोड होना
Hard Disk के first sector (MBR) से bootloader program load होता है
Examples: GRUB (Linux), NTLDR (Windows)
OS Kernel लोड होना
Operating System का main part memory में load होता है
Device drivers start होते हैं
लॉगिन स्क्रीन आना
OS पूरी तरह load हो जाता है
user login के लिए तैयार होता है
कोल्ड बूटिंग (Cold Booting)
कंप्यूटर को complete shut down के बाद start करना
full startup process होता है
वार्म बूटिंग (Warm Booting)
कंप्यूटर को restart करना
POST process skip हो सकता है
Ctrl + Alt + Delete दबाने से होता है
BIOS - Basic Input Output System (पुराना तरीका)
UEFI - Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (नया तरीका)
MBR - Master Boot Record (Hard Disk का पहला हिस्सा)
Bootloader - OS को load करने वाला program
Kernel - OS का दिमाग
BIOS की जगह UEFI आया है
तेज बूटिंग होती है
बेहतर सुरक्षा features
बड़ी Hard Disks को support करता है
ग्राफिकल इंटरफेस होता है
Boot Device Not Found - Hard Disk detect नहीं होना
Operating System Not Found - OS corrupt होना
BOOTMGR is Missing - Windows boot manager missing
Black/Blue Screen - Serious error आना
Startup Programs कम करें
SSD Hard Disk use करें
Regular Updates install करें
Unnecessary Services disable करें
Disk Cleanup regularly करें
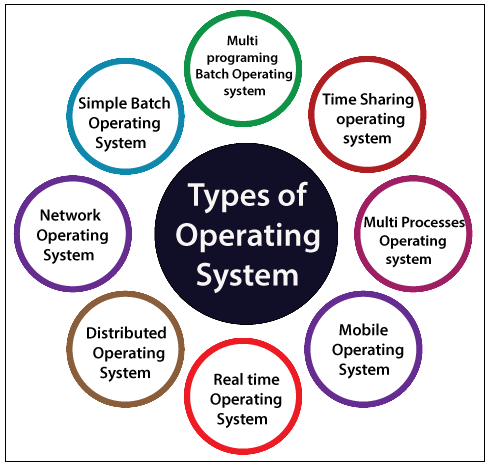
1. बैच सिस्टम (Batch Systems)
बैच सिस्टम ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम का सबसे पुराना प्रकार है जिसमें similar प्रकार के jobs को groups (batches) में इकट्ठा करके process किया जाता था। इसमें user की direct interaction नहीं होती थी।
कल्पना कीजिए एक लाइब्रेरी में:
सभी students अपना homework (jobs) librarian को देते हैं
Librarian similar subjects के homework को groups में बाँटता है (batch बनाता है)
फिर एक-एक group को teacher के पास check करने के लिए भेजता है
Students को तुरंत result नहीं मिलता, उन्हें बाद में मिलता है
यही बैच सिस्टम का basic idea है।
No Direct Interaction
User और computer के बीच कोई direct interaction नहीं
User job submit करके बाद में result collect करता है
Batch Formation
Similar jobs को groups में organize किया जाता था
Example: सभी FORTRAN programs एक batch, सभी COBOL programs दूसरी batch
First-Come-First-Serve
Jobs को sequential order में process किया जाता था
जो job पहले आती, उसे पहले process किया जाता
Offline Operation
Input devices (card readers) और output devices (printers) separately operate होते थे
Job Submission → User job punch cards पर prepare करता है
Batch Formation → Operator similar jobs को इकट्ठा करता है
Loading → Batch को computer में load किया जाता है
Execution → Jobs sequential execute होती हैं
Output → Results printer पर print होते हैं
Single-Stream Batch Systems
एक समय में एक ही job execute होती थी
बहुत slow processing
Multi-Stream Batch Systems
Multiple jobs एक साथ execute होती थीं
Better resource utilization
High Throughput - बिना interruption के continuous processing
Resource Sharing - Multiple users resources share कर सकते थे
Simple Management - Operation और management आसान
Cost Effective - Expensive computers का better utilization
No Interactivity - User job submit करने के बाद change नहीं कर सकता
Long Turnaround Time - Result मिलने में घंटों या दिनों लगते थे
Debugging Difficult - Errors का पता लगाना मुश्किल
CPU Idle Time - I/O operations के दौरान CPU idle रहता था
IBM's OS/360 - Mainframe computers के लिए
UNIVAC I - पहला commercial computer
Early FORTRAN Systems - Scientific calculations के लिए
आज भी बैच प्रोसेसिंग का use होता है:
Payroll Systems - Employee payments process करना
Bank Statements - End-of-day transactions process करना
Bill Generation - Monthly bills generate करना
Data Processing - Large datasets process करना
1950s-1960s में developed
Mainframe Computers के लिए designed
Punch Cards और Magnetic Tapes का use
Computer Operators की required होती थी
2. इंटर-एक्टिव सिस्टम (Interactive Systems)
इंटरएक्टिव सिस्टम (Interactive Systems) in Operating System
इंटरएक्टिव सिस्टम वे ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम हैं जो user को real-time में computer के साथ interact करने की facility provide करते हैं। User commands देता है और system immediately respond करता है।
कल्पना कीजिए एक रेस्तरां में:
बैच सिस्टम → Pre-set menu (जो पहले से तय है)
इंटरएक्टिव सिस्टम → À la carte menu (जहाँ आप order करते हैं और तुरंत बनकर आता है)
यहाँ user (ग्राहक) अपनी choice के according order देता है और तुरंत response मिलता है।
Real-Time Interaction
User commands देता है, system तुरंत respond करता है
Immediate feedback मिलता है
Direct Communication
User और computer के बीच direct interface होता है
No delay in communication
Quick Response Time
Fast response expected होता है
Typically few seconds से कम
User-Friendly Interface
Graphical User Interface (GUI) होता है
Easy to use और learn
Command-Line Interfaces (CLI)
Text-based commands
Examples: UNIX shell, DOS prompt
Powerful लेकिन technical knowledge required
Graphical User Interfaces (GUI)
Visual interfaces with icons और windows
Examples: Windows, macOS, Linux desktop environments
Beginner-friendly और intuitive
Input Devices
Keyboard, mouse, touchscreen
User input के लिए
Output Devices
Monitor, speakers
System response के लिए
User Interface
CLI या GUI
Interaction का medium
Response Handler
Immediate processing के लिए
Quick response generate करता है
Immediate Feedback - User को तुरंत response मिलता है
Error Correction - Mistakes immediately correct कर सकते हैं
User Control - User process control कर सकता है
Better Debugging - Real-time problem solving
Higher Productivity - Faster task completion
Resource Intensive - More memory और processing power required
Complex Design - Implementation complex होता है
Security Concerns - Direct access security risks बढ़ाता है
Response Time Maintenance - Consistent performance maintain करना challenging
Modern Desktop OS
Windows 10/11
macOS
Linux with GUI (Ubuntu, Fedora)
Smartphone OS
Android
iOS
Web Browsers
Chrome, Firefox
Interactive web applications
Video Games
Real-time user interaction
Immediate feedback
ATMs - Immediate transaction processing
Point-of-Sale Systems - Real-time sales processing
Online Gaming - Real-time multiplayer interaction
Interactive Learning Systems - Immediate feedback on answers
Customer Service Chatbots - Real-time customer interaction
3. मल्टीप्रोग्रामिंग (Multiprogramming)
मल्टीप्रोग्रामिंग एक ऐसी technique है जहाँ एक से अधिक programs को एक साथ memory में load किया जाता है और CPU एक समय में एक ही program execute करता है, लेकिन जब एक program wait करता है (जैसे I/O operation के लिए), तो CPU दूसरे program को execute करता है।
कल्पना कीजिए एक रसोई में:
एक cook (CPU) है
कई dishes (programs) एक साथ बन रही हैं
जब एक dish oven में bake हो रही होती है (I/O wait), cook दूसरी dish prepare करता है
इस तरह cook का time waste नहीं होता
यही multiprogramming का concept है।
CPU Utilization बढ़ाना
System Throughput improve करना
Resource Sharing सक्षम करना
System Efficiency बढ़ाना
1. बैच प्रोसेसिंग सिस्टम (Batch Processing Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Similar jobs को batches में process किया जाता है
No user interaction during execution
High throughput
First-Come-First-Serve scheduling
उदाहरण: IBM OS/360, Early Mainframe Systems
2. टाइम-शेयरिंग सिस्टम (Time-Sharing Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Multiple users एक साथ system use करते हैं
CPU time small slices में divided होता है
Quick response time required
Interactive computing
उदाहरण: UNIX, MULTICS, Linux
3. रियल-टाइम सिस्टम (Real-Time Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Strict timing constraints
Immediate response required
Predictable behavior essential
Two types: Hard real-time और Soft real-time
उदाहरण: Air Traffic Control, Medical Systems, Industrial Robots
4. मल्टीप्रोसेसिंग सिस्टम (Multiprocessing Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Multiple CPUs एक साथ काम करते हैं
True parallel execution
High reliability और performance
Symmetric और Asymmetric types
उदाहरण: Windows NT, Linux SMP Systems
5. डिस्ट्रिब्यूटेड सिस्टम (Distributed Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Multiple computers network से connected
Resource sharing across network
Fault tolerance और scalability
Transparency provided
उदाहरण: Cloud Computing Systems, Distributed Databases
6. नेटवर्क ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम (Network Operating Systems)
विशेषताएँ:
Multiple computers network में connected
File और resource sharing
Centralized management
Examples include Windows Server, Novell NetWare
Increased CPU Utilization - CPU idle time कम होता है
Higher Throughput - More jobs completed per unit time
Efficient Resource Use - Better memory और I/O device utilization
Improved Response Time - Better system responsiveness
Memory Management - Multiple programs को memory में manage करना
CPU Scheduling - Fair और efficient scheduling required
Deadlock Handling - Resource conflicts resolve करना
Protection और Security - Programs को एक-दूसरे से protect करना
Memory Protection - Programs interfere न करें
CPU Scheduling - Fair time allocation
I/O Management - Efficient device handling
File Management - Organized storage access
All Modern Operating Systems multiprogramming support करते हैं
Context Switching के through achieve होता है
Virtual Memory technique के साथ combine होता है
Process Management का essential part
4. टाइम-शेयरिंग कम्प्यूटिंग (Time-sharing computing)
टाइम-शेयरिंग सिस्टम एक प्रकार का ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम है जो multiple users को एक ही computer system के साथ simultaneously interact करने की capability provide करता है। यह CPU time को small intervals (time slices) में divide करके हर user को बारी-बारी से CPU time allocate करता है।
कल्पना कीजिए एक शिक्षक (CPU) है जो कई students (users) को एक साथ पढ़ा रहा है:
Teacher हर student को थोड़ा-थोड़ा time देता है
Quickly एक student से दूसरे student की ओर switch करता है
सभी students को लगता है कि teacher सिर्फ उन्हीं पर attention दे रहा है
यह switching इतनी fast होती है कि किसी को wait नहीं करना पड़ता
यही time-sharing का basic concept है।
Multiple User Support
एक साथ कई users system use कर सकते हैं
प्रत्येक user को independent environment मिलता है
Quick Response Time
Fast response expected होता है (कुछ seconds से कम)
Users को immediate feedback मिलता है
Time Slicing
CPU time को small quantum में divide किया जाता है
प्रत्येक user को बारी-बारी से time slice मिलता है
Interactive Computing
Real-time user interaction possible होता है
Users commands दे सकते हैं और immediate response पा सकते हैं
CPU Scheduling
Round Robin scheduling algorithm
Small time quantum (10-100 milliseconds)
Memory Management
Virtual memory technique
Swapping और paging
File Management
Concurrent file access
Protection mechanisms
I/O Management
Buffering और spooling
Device sharing
Cost Effective - Expensive resources का sharing
Quick Response - Immediate user feedback
Resource Sharing - Multiple users resources share कर सकते हैं
Reduced Idle Time - CPU का better utilization
Convenience - Users अपने convenience के according work कर सकते हैं
Complex Scheduling - Efficient CPU scheduling required
Security Issues - User data protection जरूरी
Memory Management - Multiple programs को manage करना
Overhead - Context switching का overhead
Resource Contention - Limited resources के लिए competition
UNIX - First successful time-sharing system
MULTICS - Time-sharing का pioneer
Linux - Modern time-sharing capabilities
Windows Server - Multiple user support
VMware - Virtual machine time-sharing
Fast Hardware - Quick context switching के लिए
Large Memory - Multiple programs store करने के लिए
Protection Mechanisms - Users को एक-दूसरे से protect करना
Scheduling Algorithms - Fair time allocation के लिए
Cloud Computing - Multiple users shared resources use करते हैं
Virtualization - Single physical machine multiple virtual machines run करती है
Web Servers - Multiple clients simultaneously serve होते हैं
Database Systems - Concurrent user access
Online Gaming - Real-time multiplayer interaction
5. मल्टीप्रोसेसिंग (Multiprocessing)
मल्टीप्रोसेसिंग सिस्टम एक ऐसा ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम है जो एक से अधिक CPUs (Processors) का एक साथ उपयोग करता है। इसमें multiple processors एक common physical memory और peripheral devices share करते हैं, और एक ही समय में एक से ज्यादा processes execute हो सकती हैं।
कल्पना कीजिए एक बड़ी रसोई में:
एक अकेला chef (Single CPU) → सारा काम अकेले करता है
कई chefs एक साथ (Multiple CPUs) → हर chef अलग-अलग dish बनाता है
सभी chefs एक ही kitchen (Memory) share करते हैं
ज्यादा dishes एक साथ बनती हैं → ज्यादा काम होता है
यही multiprocessing का basic concept है।
Parallel Execution
Multiple processes एक साथ execute होती हैं
True parallel processing possible होता है
Shared Memory
सभी processors एक common memory share करते हैं
Data sharing आसान होता है
Increased Throughput
More work completed in less time
System efficiency बढ़ती है
Enhanced Reliability
एक processor fail होने पर दूसरे काम करते रहते हैं
Fault tolerance capability
1. Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP)
विशेषताएँ:
सभी processors equal होते हैं
कोई master-slave relationship नहीं
सभी processors same memory access कर सकते हैं
Load balancing automatically होता है
उदाहरण: Modern Windows, Linux, macOS
2. Asymmetric Multiprocessing (AMP)
विशेषताएँ:
Processors asymmetric होते हैं
Master processor control करता है, slave processors काम करते हैं
No memory sharing between processors
Simpler design लेकिन less efficient
उदाहरण: Embedded systems, Special-purpose computers
Multiple CPUs/Cores
Physical processors या processor cores
Parallel execution capability
Shared Memory
Common address space
Inter-process communication
Interconnection Hardware
Processors को connect करने वाला infrastructure
Buses, crossbar switches
Symmetric Memory Access
Uniform memory access time
Consistent performance
Higher Performance - More processors, more processing power
Better Reliability - Fault tolerance capability
Economic Scaling - Cost-effective performance improvement
Enhanced Throughput - More tasks completed simultaneously
Improved Response Time - Faster task completion
Complex Scheduling - Multiple processors के लिए efficient scheduling
Memory Coherence - Data consistency maintain करना
Inter-Processor Communication - Processors के बीच coordination
Deadlock Handling - Resource conflicts resolve करना
Software Compatibility - Parallel programming support required
Windows NT/10/11 - SMP support
Linux - Symmetric multiprocessing
macOS - Multiple processor support
UNIX Systems - Enterprise-level multiprocessing
Database Servers - Oracle, SQL Server
Hardware Support
Multiple processors वाला motherboard
Cache coherence mechanisms
OS Support
Parallel scheduling algorithms
Memory management for shared memory
Software Support
Multithreaded applications
Parallel programming libraries
Scientific Computing - Complex simulations और calculations
Database Management - Large-scale data processing
Web Servers - High traffic handling
Video Editing - Real-time video processing
Gaming - High-performance graphics rendering
6. मल्टीटास्किंग (Multitasking)
मल्टीटास्किंग सिस्टम एक ऐसा ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम है जो एक ही समय में multiple tasks या processes को execute करने की capability provide करता है। यह single CPU का efficient use करके user को यह illusion देता है कि multiple programs simultaneously run हो रही हैं।
कल्पना कीजिए एक व्यस्त माँ (CPU) है जो:
एक hand से cooking कर रही है (एक program)
दूसरी hand से baby को feed कर रही है (दूसरा program)
Phone पर बात कर रही है (तीसरा program)
Quickly एक काम से दूसरे काम में switch कर रही है
यह switching इतनी fast होती है कि सबको लगता है कि सभी काम एक साथ हो रहे हैं। यही multitasking का concept है।
Concurrent Execution
Multiple tasks apparently simultaneously execute होती हैं
Rapid switching between tasks
Efficient CPU Utilization
CPU idle time minimize होता है
Better resource management
User Convenience
एक साथ multiple applications use कर सकते हैं
Example: Browser, Word, Music player एक साथ चलना
Quick Response
Immediate task switching
Smooth user experience
1. Cooperative Multitasking
विशेषताएँ:
Tasks voluntarily CPU release करती हैं
एक task CPU hold करके दूसरों को block कर सकती है
Simpler implementation
उदाहरण: Early Mac OS, Windows 3.x
2. Preemptive Multitasking
विशेषताएँ:
OS control में task switching होता है
Time slices allocate करता है
एक task दूसरी task को block नहीं कर सकती
Better stability
उदाहरण: Modern Windows, Linux, macOS
Increased Productivity - एक साथ multiple applications use कर सकते हैं
Efficient Resource Use - CPU का optimal utilization
Better Responsiveness - System hang नहीं होता
Time Saving - Multiple tasks parallel handle होती हैं
Improved User Experience - Smooth और seamless operation
Task Scheduler
Tasks के बीच switching manage करता है
Priority-based scheduling
Memory Management
Multiple tasks को memory allocate करता है
Virtual memory support
Context Switching
एक task का state save करके दूसरी task load करता है
Fast और efficient switching
Inter-Process Communication
Tasks के बीच data sharing enable करता है
Modern Windows OS (10, 11)
एक साथ multiple apps run करना
Browser, Office, Games simultaneously
Linux Desktop Environments
Multiple windows और applications
Background services
macOS
Smooth multitasking experience
Mission Control feature
Smartphone OS
Android और iOS में background apps
Quick app switching
Fast Processor - Quick context switching के लिए
Adequate RAM - Multiple programs store करने के लिए
Efficient Scheduler - Fair time allocation के लिए
Memory Protection - Programs interfere न करें
Video Editing - Editing के साथ rendering
Gaming - Game के साथ voice chat
Programming - Coding के साथ compilation
Office Work - Documents, spreadsheets, presentations एक साथ
Content Creation - Design, writing, research simultaneously
7. मल्टी यूसर ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम (Multi user Operating System)
मल्टी यूजर ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम एक ऐसा ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम है जो एक ही समय में एक से अधिक यूजर्स को कंप्यूटर सिस्टम का उपयोग करने की अनुमति देता है। प्रत्येक यूजर को अपना अलग यूजर अकाउंट और वर्किंग एनवायरनमेंट मिलता है।
कल्पना कीजिए एक बड़ा ऑफिस:
एक central computer system (सर्वर)
कई employees (यूजर्स) अपने-अपने कंप्यूटर्स से connect होते हैं
हर employee का अलग login ID और password होता है
सभी एक ही system के resources use करते हैं
लेकिन हर किसी की files और settings अलग होती हैं
यही multi-user system का concept है।
Multiple User Access
एक साथ कई यूजर्स system use कर सकते हैं
प्रत्येक यूजर को unique user account मिलता है
Resource Sharing
Hardware resources (printer, scanner) share होते हैं
Software applications और data share होते हैं
Time-Sharing
CPU time को small slices में divide किया जाता है
प्रत्येक यूजर को बारी-बारी से time मिलता है
Security और Privacy
User authentication required
Data protection और access control
1. टाइम-शेयरिंग सिस्टम
विशेषताएँ:
Interactive user sessions
Quick response time
Examples: UNIX, Linux
2. डिस्ट्रिब्यूटेड सिस्टम
विशेषताएँ:
Multiple computers network से connected
Resource sharing across locations
Examples: Cloud systems
3. सेंट्रलाइज्ड सिस्टम
विशेषताएँ:
Mainframe-based systems
Terminal-based access
Examples: IBM mainframes
User Management
User accounts create और manage करना
Authentication और authorization
Resource Manager
CPU, memory, devices allocate करना
Fair resource distribution
File System
User files organize करना
Access permissions manage करना
Network Services
Remote access enable करना
Data sharing facilitate करना
Cost Effective - Expensive resources का sharing
Centralized Management - Easy administration और maintenance
Collaboration - Users के बीच easy data sharing
Scalability - नए users easily add किए जा सकते हैं
Consistency - सभी users को same software environment
Security Risks - Unauthorized access का खतरा
Performance Issues - Heavy load पर slow performance
Complex Configuration - Setup और maintenance complex
Resource Contention - Limited resources के लिए competition
Data Privacy - User data protect करना
Linux/UNIX - Classic multi-user systems
Windows Server - Enterprise multi-user support
macOS Server - Apple's multi-user solution
Cloud Platforms - AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Database Servers - Oracle, MySQL
Powerful Hardware - Multiple users handle करने के लिए
Network Infrastructure - Connectivity के लिए
User Authentication - Login security के लिए
Resource Monitoring - Performance maintain करने के लिए
Enterprise Systems - Office networks
Educational Institutions - Computer labs
Banking Systems - Branch banking solutions
Hospital Systems - Patient records management
E-commerce Platforms - Multiple concurrent users
आपरेटिंग सिस्टम के कार्य (Work of the Operating System)
ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम के मुख्य कार्य
ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम कंप्यूटर के संसाधनों का प्रबंधन करता है और यूजर तथा हार्डवेयर के बीच इंटरफेस का काम करता है। इसके प्रमुख कार्य हैं:
कार्य: Programs के execution को manage करना
उदाहरण:
Processes create और delete करना
CPU scheduling करना
Process synchronization
Deadlock handling
कार्य: Primary memory का efficient use सुनिश्चित करना
उदाहरण:
Memory allocate और deallocate करना
Virtual memory manage करना
Memory protection provide करना
कार्य: Data storage और retrieval manage करना
उदाहरण:
Files create, delete और organize करना
Directory structure maintain करना
Backup और recovery
कार्य: Input/output devices control करना
उदाहरण:
Device drivers manage करना
Device allocation और deallocation
Buffering और spooling
कार्य: System और data protect करना
उदाहरण:
User authentication
Access control
Encryption और decryption
कार्य: Network communication manage करना
उदाहरण:
Network connections establish करना
Data transmission manage करना
Network security provide करना
कार्य: User commands को execute करना
उदाहरण:
Command line interface provide करना
Graphical user interface provide करना
System calls handle करना
कार्य: System performance track करना
उदाहरण:
Resource usage monitor करना
Performance statistics maintain करना
System optimization
कार्य: System errors detect और handle करना
उदाहरण:
Hardware errors detect करना
Software errors handle करना
Error messages display करना
कार्य: System resources fairly distribute करना
उदाहरण:
CPU time allocate करना
Memory space distribute करना
I/O devices allocate करना
Efficiency - Resources का optimal use
Convenience - User-friendly interface
Security - Data protection
Reliability - Stable operation
Scalability - Future expansion support
We are accepting Guest Posting on our website for all categories.
I want to Hire a Professional..
Sanjeev panday
@DigitalDiaryWefru